In today’s society, laser welding technology is increasingly becoming an important and eye-catching process in manufacturing. The importance of welding cannot be overstated. Laser welding is known for its high precision, efficiency and wide applicability. This technology has achieved remarkable success in various fields.
This article will explore the application areas of laser welding technology to gain insight into the importance of this advanced manufacturing technology. From automobile manufacturing to the electronics industry, from medical equipment to aerospace, laser welding is bringing unprecedented changes to all walks of life. An in-depth understanding of the specific application of laser welding technology in various industries is of great significance for us to better understand the precision technology behind modern manufacturing.
5 Applications of Laser Welding in Industries
Automotive Industry
- Body Manufacturing: Laser welding plays a vital role in automobile body manufacturing. It enables highly precise welding. This allows the car body to be lighter while maintaining structural strength. The lightweight design helps improve fuel efficiency and reduce exhaust emissions. This is in line with the modern automotive industry’s continuous pursuit of environmental protection and energy efficiency.
- Parts Manufacturing: Laser welding is widely used to manufacture automotive parts, especially for parts with complex shapes and high strength requirements. For example, engine components, suspension systems, exhaust systems, etc. The high-strength welding requirements of these components can be achieved through the high energy density and precision of laser welding.
- Welding Aluminum Alloys: As the demand for lightweight materials in automobile manufacturing increases, the application of aluminum alloys in automobile manufacturing has gradually expanded. Laser welding technology excels at welding aluminum alloys. Because it can effectively connect aluminum alloy parts without generating too much thermal impact, ensuring weld quality and structural strength.
- Car Lamp Manufacturing: Laser welding technology is also widely used in the manufacturing process of automobile lighting systems, especially LED lamps. Laser welding can achieve efficient connection of small and complex parts, ensuring the reliability and performance of car lights.
- Highly Automated Production Lines: The automated nature of laser welding makes it ideal for use in highly automated production lines. In automobile manufacturing, laser welding technology can achieve high-efficiency production of a large number of parts. This increases efficiency and reduces labor costs.
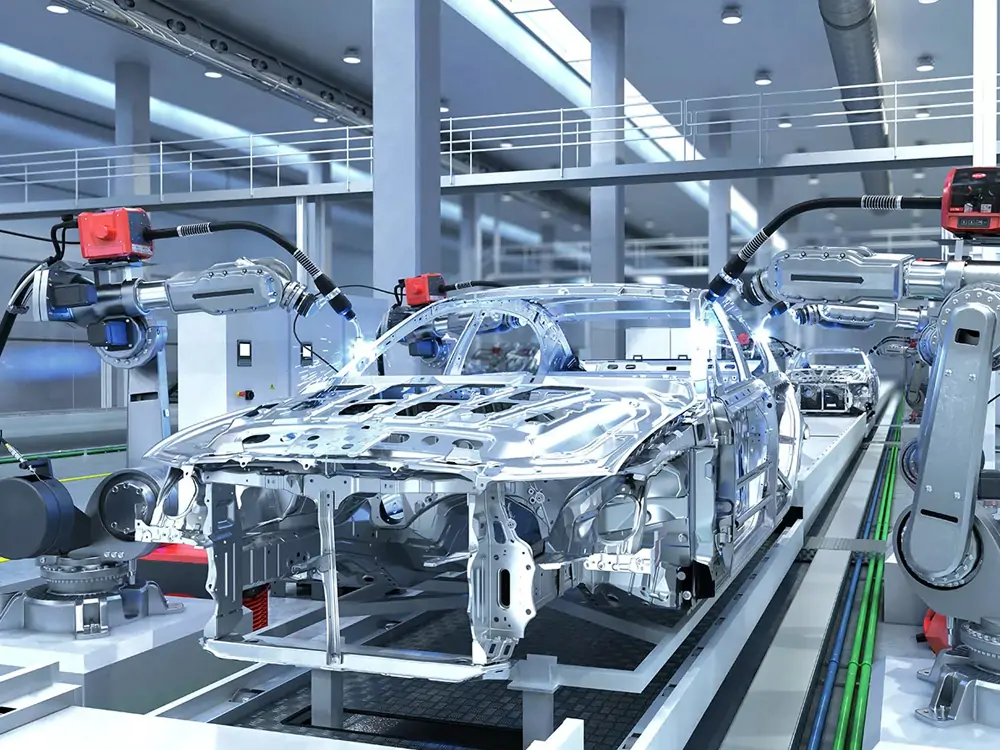
Aerospace Industry
- Manufacturing Lightweight Structures: The aerospace industry has very high requirements for lightweight materials. Because there is a need to improve the fuel efficiency and performance of aircraft. Laser welding can reduce the weight of components without losing material strength by enabling highly precise welds. It therefore provides greater flexibility in spacecraft design.
- System Manufacturing: The manufacturing of engine components and propulsion systems places extremely high demands on welding processes. Because these components must be able to withstand extreme temperatures, pressures and mechanical loads. The high energy density and local heating effect of laser welding enable precision welding on special materials such as high-temperature alloys. This ensures the reliability and durability of the propulsion system.
- Structural Assembly: Spacecraft are often composed of complex structures. The high degree of automation and high efficiency of laser welding make it an ideal choice for fast and reliable connection of large structural parts. This is critical to improving production efficiency, reducing costs and ensuring manufacturing quality.

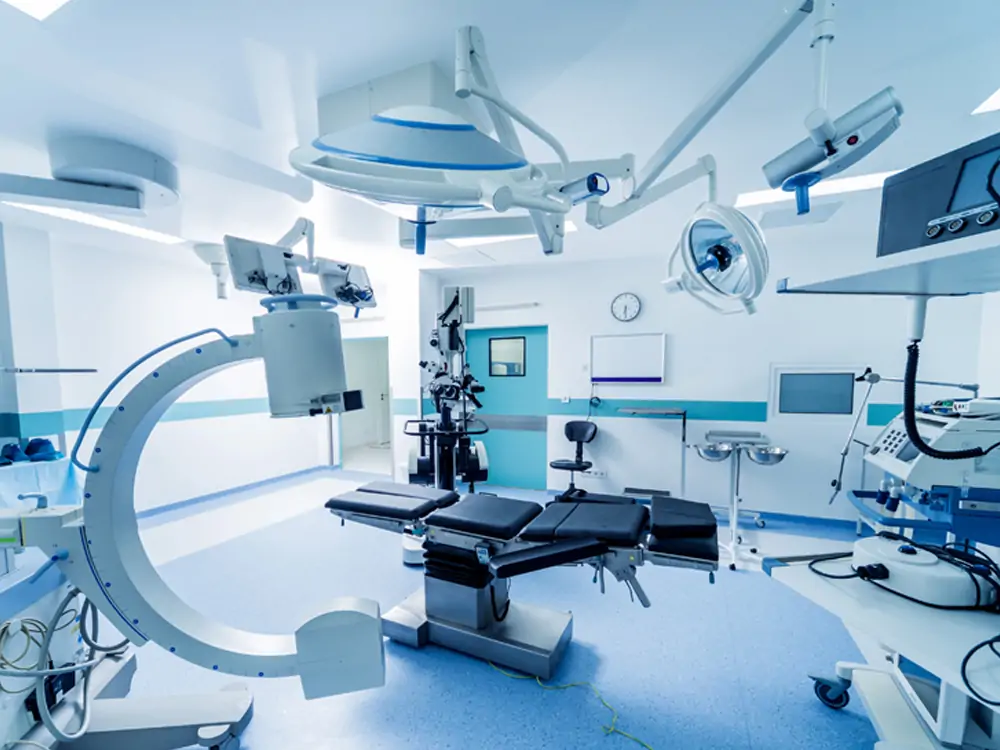
Medical Device Manufacturing
- Precision Instrument Manufacturing: The high precision and non-contact nature of laser welding make it the technology of choice when it comes to manufacturing precision medical instruments. For example, micro-instruments used in surgeries, optical equipment and components of laser systems require highly precise medical equipment, and laser welding can achieve tiny solder joints. This avoids the loss of accuracy that can occur with traditional welding methods.
- Biomaterial Joining: In the biomedical field, laser welding is widely used to join biomaterials. Examples include different types of tissue or biological implants. This welding method enables precise connections and reduces thermal damage to biomaterials, thus maintaining their original biological properties.
- Medical Device Assembly: Medical devices often contain complex structures. The high degree of automation and high efficiency of laser welding make it an ideal choice for assembling large instruments. This includes the assembly of large medical equipment such as X-ray machines and MRI equipment. Laser welding ensures the structural rigidity and stability of these devices.
- Medical Device Repair: Laser welding is also used in the repair and maintenance of medical devices. For some expensive and complex medical devices, laser welding technology can accurately repair damaged or worn parts. This extends the life of the equipment and reduces replacement costs.
Energy Industry
- Pipe Welding: In the oil and gas industry, laser welding is widely used to weld pipes. Including oil pipelines and natural gas pipelines. Laser welding provides highly precise weld seam control. It reduces welding deformation and residual stress, improving the reliability and durability of the pipeline.
- Nuclear Energy Equipment Manufacturing: In the nuclear energy industry, laser welding is used to manufacture nuclear reactor components, nuclear power plant pipes and vessels. The high precision and low heat input of laser welding help ensure weld quality. In addition, it can reduce adverse effects on materials and improve the safety and reliability of nuclear energy equipment.
- Wind Energy Equipment Manufacturing: Laser welding is used in the wind energy industry to manufacture wind turbine components, including blades and towers. Laser welding can ensure the structural stability and dynamic balance of the wind blades, improving the performance and life of the wind turbine.
- Solar Cell Manufacturing: In the solar industry, laser welding is used to join solar cells and manufacture solar modules. Laser welding provides an efficient way to join. It reduces the thermal impact on solar cells and helps improve the conversion efficiency of solar cells.
- Electrical Equipment Repair: Laser welding can be used for the repair and restoration of electrical equipment. This includes welding equipment such as generator sets, transmission lines and transformers. It can effectively repair damaged or aging parts, extend the life of equipment and reduce downtime.
- Energy Pipe And Vessel Manufacturing: In energy transmission and storage, laser welding is used to weld a variety of pipes and vessels. Such as oil tanks, gas tanks and gas storage. Laser welding can ensure the high quality of welds and improve the safety and reliability of pipes and containers.

Electronics Industry
- Circuit Board Manufacturing: Laser welding is widely used to connect electronic components to printed circuit boards (PCBs). Laser welding enables highly precise control of tiny solder joints. This ensures reliable connections between electronic components, especially in the manufacture of high-density integrated circuits.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: In the semiconductor industry, laser welding is used to join and package tiny chips and sensors. It provides highly precise connections to microelectronic devices. At the same time, it reduces the thermal impact on the device and helps maintain device performance.
- Manufacturing of Laser Diodes (LDs) And Lasers: Laser welding plays a key role in the manufacturing of laser diodes and other lasers. It is used to connect and encapsulate the various components of the laser, ensuring highly stable and reliable laser output.
- Connecting Micro Electronic Components: Laser welding is a very effective joining technology for micro electronic components such as micromotors, microsensors and microconnectors. It can achieve highly precise welding on a microscopic scale and is suitable for use in the field of micro-nano technology.
- Optical Device Manufacturing: Laser welding is used to assemble and join precision optical components when manufacturing optical components and optical communication equipment. This ensures the efficiency and accuracy of the optical system.
- Electronic Packaging: In the electronic packaging process, laser welding is used to join the casing of the packaged device. This ensures device sealing and durability.
- Flexible Electronics Manufacturing: For flexible electronic components, such as flexible circuit boards and connections in wearable devices, laser welding enables precise welding of thin-film materials. This ensures flexibility and stability of the device.

Advantages And Disadvantages of Laser Welding
Laser welding is an advanced welding technology. It is widely used in many fields because of its superior performance. In fact, laser welding has many advantages but also some limitations. Let’s explore the main advantages and disadvantages of laser welding.
Laser Welding Advantages
- High Precision: Laser welding enables very small and precise welding joints. It is suitable for applications requiring highly precise connections, such as electronic devices and micro-components.
- Non-contact: Laser welding is a non-contact welding process. It does not require direct contact with the workpiece surface, thus avoiding possible contamination or damage caused by physical contact.
- High Energy Density: Laser has high energy density, which allows it to heat the welding area quickly. It enables fast welding and is particularly suitable for materials that are sensitive to heat input.
- High Efficiency: Due to the high energy density of laser welding, the welding process can be completed in a short time, improving production efficiency.
- Narrow Welding Seams And Low Thermal Influence: Laser welding can achieve very narrow welding seams. This reduces the material’s heat-affected zone and helps maintain the material’s original properties.
- Suitable For A Variety of Materials: Laser welding is suitable for a variety of materials. Including metals, plastics, ceramics, etc., with strong versatility.
Laser Welding Disadvantages
- High Equipment Costs: The purchase and maintenance costs of laser welding equipment are relatively high. This may limit adoption by manufacturers with smaller production runs or more limited budgets.
- Sensitive to Workpiece Positioning: Laser welding has high requirements on the positioning and alignment of workpieces. If the workpiece is not positioned accurately, it can result in poor welding quality.
- Transparent Materials Are Difficult to Process: Transparent materials are difficult for lasers to penetrate. Therefore, it is difficult to weld transparent or translucent materials.
- Limited By Material Thickness: Laser welding has certain limitations on the thickness of the material. For thicker workpieces, multiple passes of welding may be required.
- Sensitive to The Environment: Laser welding has high environmental requirements and needs to be carried out in a relatively clean environment to avoid the impact of dust or impurities on the welding quality.
Conclusion
In this article, we take an in-depth look at the wide range of applications of laser welding technology in different fields. From automobile manufacturing to medical devices, from aerospace to electronics industries, laser welding has shown great potential with its high precision, high efficiency and multi-material applicability. This advanced welding technology not only promotes innovation in manufacturing, but also brings new manufacturing standards to modern industry.
In the future, we can expect to see laser welding playing a key role in more areas and making greater contributions to the sustainable development of manufacturing. At the same time, we should also continue to pay attention to the innovation and improvement of laser welding technology to continuously meet the increasing needs of different industries for the precision and efficiency of manufacturing processes.